Causes of udder edema in goats
Lamb is a big load on the animal organism. If the goat is pregnant for the first time, then the cloven-hoofed animal should be constantly monitored. Farmers and breeders often notice udder edema in a goat during pregnancy or after childbirth.
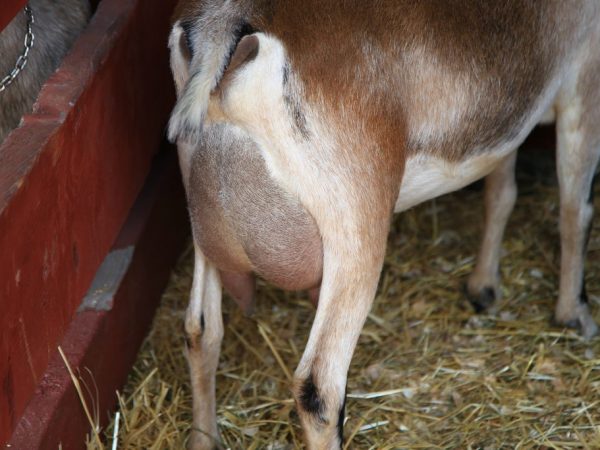
Causes of udder edema in goats This is largely due to the structure of the body of an artiodactyl, but in some cases, udder compaction may be due to improper start-up or diseases. These problems can lead to milk loss. Swelling of the udder in a goat after lambing may appear in the case of improper milk production. This can happen due to non-compliance with the preparation of the animal for childbirth.
Causes of udder edema
Udder edema is called hardening and swelling of the milk ducts in the mammary glands due to a hormonal disorder in the body of an artiodactyl. Usually, this kind of trouble happens to animals during pregnancy or after lambing. The most common cause of udder edema is considered lack of movement and walking during pregnancy, as well as too much silage and succulent feed in the daily diet of females. Edema of the mammary glands may not be associated with pregnancy and lambing, in this case, its cause is non-compliance with sanitary standards for milking or illness. A few days before lambing and the same number of days after the udder of an animal may swell due to a strong blood flow. However, swelling during pregnancy or a month later is not considered normal. This may be due to toxicosis or weakening of the heart and kidneys during pregnancy.
It also depends on the age of the goat. If this first lambing is in an artiodactyl, then edema may occur a week or two before childbirth, since the circulatory system adapts to the animal body.
Signs of udder edema in goats
First of all, the disease affects a quarter or all of the back of the udder. The skin on the swollen organ is rough, thick, and when pressed with fingers, compaction is felt. If help was not provided, then over time, the swollen udder becomes so coarse that it is impossible to press on it with your fingers. In this case, the skin becomes cold due to the compression of the blood vessels. The swelling begins in the nipples of the animal. These nipples become shorter and rougher than non-swollen nipples. Next, the edema affects the subcutaneous tissue up to the vulva. Sometimes not only the udder swells, but also the abdomen to the chest. The liquid filling the udder squeezes not only the milk ducts, but also the gastrointestinal tract, as a result of which the goat may stop eating. Squeezing blood and lymph vessels can compromise their integrity and lead to udder necrosis. In some cases, postpartum edema leads to mastitis. The body temperature and general health of the goat may be normal.
The swelling of the udder also affects the quality of the milk. It becomes watery and poorly squeezed out due to constriction of blood vessels. As a result, the amount of milk yield can be dramatically reduced, even though goats have the best lactation in the postpartum period.
Sometimes more milk can be obtained from the swollen part of the udder than from the normal one. It depends solely on the location and effect of the fluid on the vessels.
In the case of postpartum edema, it may resolve on its own within a few days after lambing. If the udder is in a swollen state for several weeks, then this is already a sign of postpartum complications. These goats have impaired lactation, they may even refuse to feed the kids.
Udder edema in artiodactyls after childbirth is considered a physiological phenomenon, but it should not be triggered. With edema of the mammary glands, the udder tissue begins to stretch, the animal's immune system decreases, which can lead to complex inflammatory processes. One of the unpleasant diseases that can affect a goat due to udder swelling is mastitis.
Mastitis as a consequence of udder edema
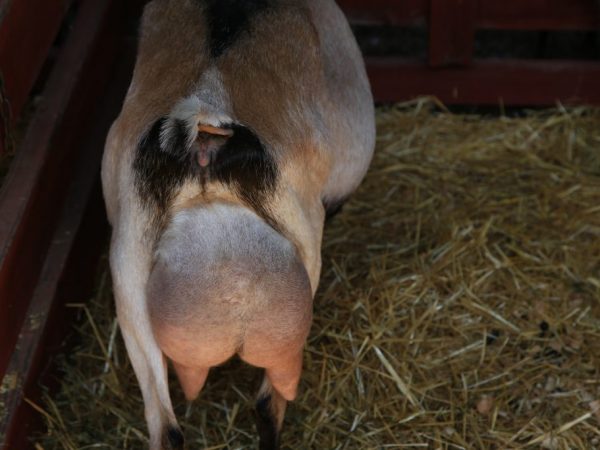
Sometimes antibiotics cannot be avoided
Goats, like many large animals on the farm, are kept for meat, wool and milk. To get the full range of each product, the animal must be properly cared for. The most unpleasant disease for dairy owners is mastitis. It significantly reduces the daily milk yield and causes discomfort to the animal. Very often, the cause of mastitis can be a neglected swelling of the udder. To correctly prescribe a course of treatment, you need to be able to distinguish one disease from another. When the udder is affected by mastitis, each subsequent milk yield makes the milk ducts tighten. The udder thickens and becomes very stiff. The temperature of the affected area rises rapidly.
With mastitis, the nipples may become clogged with flakes, and the milk itself becomes thick and may contain blood. If you pump the milk of a sick goat into a jar and leave it for several hours, then a granular sediment will fall to the bottom.
To determine if your goat is sick with mastitis, watch it for 24 hours. If, after milking, the udder begins to tighten strongly and, when pressed with fingers, does not remain deeper on the skin, then most likely the animal is sick with mastitis. When treating this disease, the main thing is efficiency, since the affected udder becomes a habitat for harmful bacteria.
Mastitis is treated with antibiotics. Medicines are administered exclusively intramuscularly. For the treatment of this disease, the following drugs are suitable:
- Benzylpenicillin (1 million ED) - Administer twice a day for five days. Before injection, the drug is diluted in proportions of two to four per adult.
- Streptomycin - injected twice a day for five days. Before injection, the drug is diluted in proportions of two to four per adult.
- Cefazolin - enter twice a day for five days. Before injection, the drug is diluted one to two per adult. This medication is not stored in a diluted form and should be used immediately.
Treatment of postpartum udder edema

You can avoid swelling with massage.
Most often, edema after lambing goes away within a week and does not require medication. If the udder is still painfully dense even after a week, and the goat is worried and gives little milk, then certain measures should be taken to reduce fluid in the body:
- in the daily ration, the rate of silage and succulent feed is reduced;
- the animal is confined to the water;
- increase the number of movements, the goat can be driven around the pen twice a day;
- frequent milking of the animal - from three to five times a day;
- the goat should be separated from the general herd to avoid unnecessary injuries;
- massage the udder every day before and after milking.
A special massage of the udder is done with warm hands in continuous movements from the nipples to the base of the udder. Do not use irritating creams or solutions. In some cases, experienced farmers recommend using petroleum jelly or baby cream.Medical treatment of prolonged edema of the udder of a goat after lambing occurs with the help of special drugs aimed at restoring blood vessels. To do this, you can use the following drugs:
- Calcium chloride solution - 150 ml is injected intravenously twice a day.
- Calcium glucanate - 100 ml is injected intravenously once a day.
- Caffeine sodium benzoate - 20 ml is injected once a day to improve heart function.
To make the edematous fluid sleep faster, poultices of their herbal dust and warm wraps are used.
If the udder has sagged under the influence of gravity, then it must be tied up with an overhead. Watch out for this - the goat can severely injure the skin if the udder is dragged along the ground. In some cases, veterinarians recommend anti-inflammatory ointments from Rigefen. These preparations are suitable for many animals.
In addition to external treatment, they also change the diet of artiodactyls. Laxative salts or magnesia, as well as diuretic decoctions, are added to the daily menu. A list of plants that are suitable for such infusions:
- Juniper berries - 100 g per liter of water. No more than 100 ml is given per day.
- Birch buds - 50 g per liter of water. A teaspoon a day.
- Field horsetail - 50 g per liter of water. A teaspoon a day.
With the help of complex treatment, edema can be removed in a week or two. However, if the udder tissue continues to fill with excess fluid, you should go to a specialized hospital. Remember that the milkiness of the animal depends on your actions. Sometimes, with severe inflammation, not just edema, but an abscess can develop.
Prevention of udder edema in goats
In order not to face this unpleasant consequence of childbirth, certain preventive actions should be taken. First, follow the rules and timing for starting your goat before lambing. A generic launch schedule looks like this:
- First week - milk once, the amount of milk is reduced to one liter.
- The second week - milking takes place once every one and a half days, the amount of milk is reduced to half a liter.
- The third week - milk yield takes place every two days, the amount of milk is reduced to three hundred grams.
- Week 4 - Milk only when needed.
However, remember that for some dairy breeds, the schedule will need to be adjusted individually.
In addition, the pregnant female should be provided with walks. The animal does not have to stand in the stall all the time. Reduce the amount of succulent forage and silage in your goat's diet - these foods are lactogenic. The diet of artiodactyls during pregnancy should contain an increased amount of concentrates and minerals.
To avoid mastitis, goats should be kept warm and free of drafts. Adhere to the sanitary rules of keeping - clean the barn every two days, and the bedding should be changed every day.
Once every six months, the stall must be completely disinfected. During milking, special hygiene should be observed - wash the udder and hands with boiled water, massage the animal and milk it correctly. Milk residues in the udder can sometimes be the cause of the swelling. After giving birth, the goat should be kept away from the herd for some time so that the goat does not accidentally injure the female while hunting.


