The structure of the mushroom mycelium and its cultivation
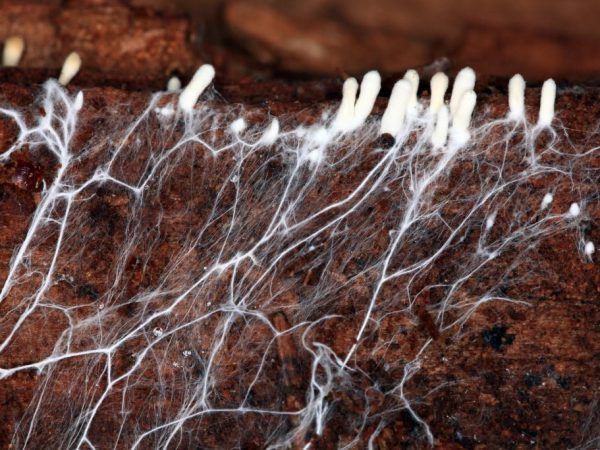
Mushrooms isolated into a separate kingdom have a special structure and vital activity. An important role in the life of fungi is played by the mycelium - a branched underground organ or partially protruding beyond the substrate, providing the fruiting body with access to nutrition and fixation in the environment.
The structure of the mushroom mycelium and its cultivation
General information and structure
The mycelium is a formation organized in the form of filaments called hyphae.
From the Greek language, the word "mycelium" is translated as "mushroom". It is a vegetative body, consisting of branched thinnest filaments and performing several functions. Outwardly, the appearance of the fungal mycelium of the highest representatives of the kingdom is similar to the root system of herbaceous plants. However, these structures have many fundamental differences:
- filament thickness from 0.5 to 10 microns;
- hyphae grow only apically (apex);
- have good growth potential - up to 35 km / y;
- the speed is different: the mucoral species are fast-growing.
The growth of hyphae is radial, which is why, from time to time, in some species of higher fungi, so-called. "Witch circles". The dense interlacing of hyphae in the fruiting body gives rise to a false feeling that this is a tissue, about the same. like plants. This formation is called "plectenchyma" or false tissue.
The mycelium of mushrooms is just one of the possible ways to form a vegetative body.
Other forms:
- Naked protoplast.
- Rhizomycelium.
- Yeast-like thallus.
- Pseudomycelium.
The second is the usual outgrowths of hyphae in organisms with a form of body organization in the form of clustered cells, with or without a membrane.
Such features can only be viewed under a microscope. The mycelium of the fungus of the genus Penicillus is similar to the mycelium of the fungus of the genus Mukor, but only similar. Non-cellular forms - naked protoplast. Their cells do not have a dense membrane of their own, and cannot be represented by mycelium.
Yeast thallus in its simplest form is a single cell. This cell has all the basic structures found in fungi. Sometimes cells can combine into various more or less strong structures in the form of a false (pseudo) or real mycelium. The sizes of single yeast cells range from 1-10 microns, more often 3-7 microns. When mycelium or elongated pseudomycelium cells are formed, their length can reach 20-50 microns, while the width remains constant and usually does not exceed 10 microns.
Varieties
The structure of the mycelium of fungi differs in different classes, one common system does not exist. The kingdom is not completely ordered: they include those who are dissimilar in appearance, method of reproduction, structure, behavior, and features of the vegetative body. Therefore, the classification is extensive and illogical.
These organisms are called multicellular and unicellular formations. In the first type, each component is clearly separated from the other, but constitutes a single tissue.
Mycelium types:
- The septic multicellular type of mycelium consists of hyphae, separated by septa - septa, in which holes are located and cytoplasm cords pass through them, connecting the cells to each other.
- Unseptic does not have such partitions and is a single whole.
According to the methods of adaptation of fungi to the environment and the peculiarities of behavior, scientists have recorded changes in the structure of the mycelium.
Responsive forms
With additional formations, the fungus improves the chances of survival and reproduction (obtaining "offspring"). Types found:
- Rhizomorphs or mycelial strands, the simple name for cords.
- Rhizoids, apressoria, and also films.
- Sclerotia.
- Haustoria and trapping hyphae.
Rhizomorphs differ from mycelial strands in power and strength, they are usually darker in color. These are hyphae growths that perform 3 functions:
- resettlement;
- protection;
- supply of nutrients.
The second type is needed by parasitic unicellular or other fungi to strengthen on the host's body, more often plants. The hyphae fit snugly against the victim's cuticle, allowing it to take root. Even according to the structure of the rhizoids, they distinguish between species.
Sclerotia are thickened hyphae covered with a dense membrane. Needed to endure extreme or unfavorable conditions. The basis for the germination of fruit bodies. Contain nutrient reserves inside.
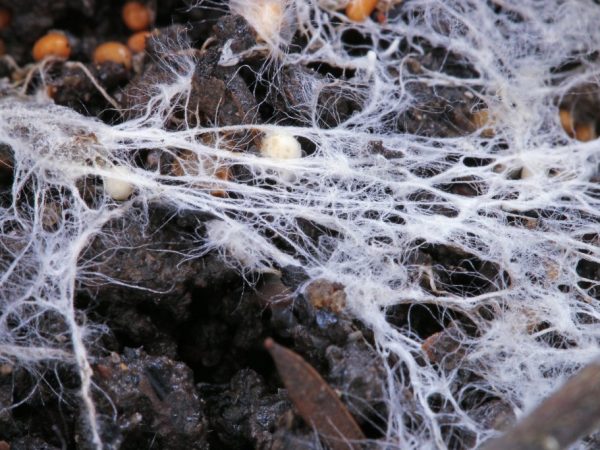

Hyphae perform the function of protection
Haustoria grow in parasitic fungi. With their help, he sucks nutrients from the host. Apressoria penetrate the host cell, and haustoria grow at their ends. And trapping hyphae are the advantage of predatory species. Their processes:
- Covered with adhesive, serves as an attachment and grip.
- Organized by loops that are sensitive to touch and movement near.
They help to survive in the most adverse conditions. Therefore, the kingdom is one of the most widespread and long-lived on Earth.
Organ functions
Mushroom mycelium has different functions:
- Strengthening in the substrate: important for the upper classes, which have a large aerial part, sensitive to external factors. Representatives of the class - white, boletus, mushrooms, etc.
- Receiving and transferring nutrients: it is necessary for all species, because fungi are either saprotrophs and receive food from substrate waste or parasites that deplete or live in symbiosis with the host, forming mycorrhiza.
- Distribution and reproduction: with the help of the mycelium, vegetative reproduction occurs. And also the organism of the fungus through hyphae containing spores in some species, multiplies over large areas.
Types of planting mycelium
To get an abundance of boletus, white, chanterelles on the site, you need to stock up on planting material. Will fit:
- grain mycelium;
- liquid mycelium;
- mycelium on wooden sticks.
The grain type of mycelium has advantages and disadvantages. Plus - the grains are light and dry material. It is used to saturate the substrate with seeds (spores). Suitable for growing fruit bodies on the ground and sawdust. Disadvantage - it works only in conditions of technological landing.
If you need to plant fruiting bodies in natural conditions (on the bark of trees), stick hyphae are suitable. They are used to infect wood cuts, and the fungus is cultivated in its natural environment on stumps. The disadvantage is that it is impossible to get large volumes of the product, it is only suitable for hardwoods.
Liquid mycelium grows first in a nutrient medium - honey, fructose. Then he moves into the external environment. The use of sealed containers and a nutrient substrate avoids the appearance of mold.
It is recommended to store blanks:
- in the refrigerator at a temperature from -1 to + 3 ℃ for no more than a month;
- at 5 ℃ no more than 3 weeks.
Violation of storage conditions leads to the fact that the cultivation of fruit mycelium is ineffective due to cell death or their premature germination.
Growing methods
Mushroom lovers very often tend to grow oyster mushroom mycelium or honey agarics with their own hands. Success depends on many factors, so you need to prepare for the procedure. The first attempts will be unsuccessful, but after observing all the rules, there is a chance of success.
Self cultivation
For growing mushrooms from mycelium in the country or in the garden, forest species are chosen. It is not only the quality of the mycelium that is important, but also the growing substrate. Many grow only on peat, coniferous, deciduous substrates, dry or swampy areas.
For the site, part of the mycelium is dug out together with the ground. Then it is placed in a wooden box with a large drainage volume. Fill in the soil of the future substrate. For domestic autumn species, the procedure is carried out in late spring or early summer.
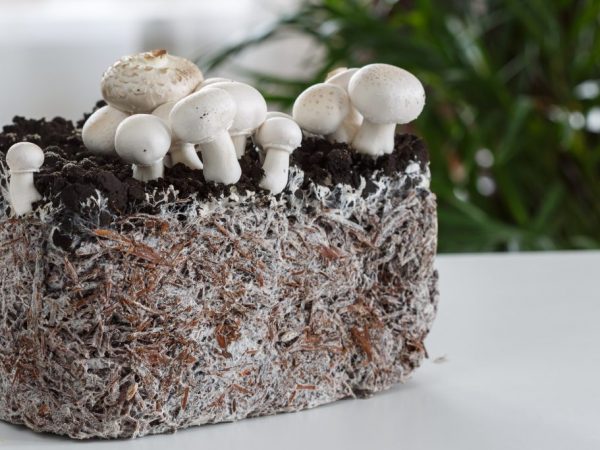

Mycelium is difficult to grow
It is necessary to maintain a certain humidity and temperature in the "incubator". Once the fine filaments have spread throughout the box, they can be transplanted into open soil. If the conditions are unfavorable, the area with the planted mycelium is covered with a film. Remember that spores of adults actively scatter and germinate; it is not easy to destroy a developed mycelium.
Individuals of the Psilocybe group are bred for different purposes - hallucinogenic fruits. During cultivation, mycelium must be kept in an airtight and sterile environment:
- They buy a jar of normal saline solution for droppers.
- The liquid is squeezed out with a syringe.
- Then a nutrient medium is placed inside - fructose.
- The presence of sterile conditions contributes to the fact that the hyphae grows for only about two days.
Champignons on cardboard
Growing mycelium at home has the following benefits:
- unfavorable for other forms;
- there is an opportunity to breathe;
- retains moisture.
Cultivation instruction:
- Soak pieces of cardboard in boiled water for an hour.
- Divide the stems of the fruiting bodies into fibers.
- Drill a drain in a plastic container.
- Divide the wet material into layers, squeeze out.
- Put the chopped champignon legs on paper, cover with a thin layer of cardboard.
- Press down to release air.
- Cover the container tightly with a bag.
Every day, the structure is ventilated and moistened as needed. You need a temperature of 20 ℃, no sunlight. The term for growth is from 20 to 60 days. Finished hyphae are placed in a nutrient medium. Stick options are also sown on cardboard in a box. The growth of mycelial cells requires a renewal of the environment, with a lack of care, it stops.
Irina Selyutina (Biologist):
Why is it better to use cardboard for growing mycelium? There are many reasons for this:
- Cardboard is made from cellulose, i.e. wood and it is familiar to the mycelium, which was already growing on wood chips or sawdust.
- Corrugated cardboard allows the developing mycelium to breathe freely.
- This substrate perfectly retains moisture.
- It doesn't need to be sterilized: just make sure there is no smell, stains, glue or writing. Just cut out these areas.
- Cardboard is available everywhere.
- It does not require a lot of effort and time to work with it.
By the way. Cardboard mycelium is a very convenient thing for growing on the balcony.
Cultivation of lower species
The lower ones are a group that is a microscopic body consisting of elongated spore-bearers and spore-bearing heads. In a lichen - a symbiosis of fungus and algae. They are also represented by mold and yeast. Most often these are pathogenic forms that threaten human health.
They are characterized by:
- fast reproduction;
- capture of the nutrient medium and its destruction;
- endurance to external conditions;
- closed-loop development.
Breeding the lower ones is much easier, they often get tea and kefir mushrooms.
To grow them at home, you need to take a base - a small part of hyphas that are already ready for independent existence. They are sold at the pharmacy or by hand. Further? must be placed in their nutrient medium - sweet tea, milk. Feeding on carbohydrates or milk constituents, fungi begin to ferment liquid.
It is necessary to collect the resulting infusion, rinse the overgrown mushrooms and update the environment.
- The tea specimen is slimy, brownish, light yellow, layered on the cut.
- The kefir specimen is spherical, always white without inclusions, non-porous and not slimy inside.
You can grow kombucha endlessly - on an industrial scale, the mass reaches 100 kg. But kefir is aging and spoils the product, so it is updated from time to time. The process is similar for mold, only the medium will be non-liquid. Certain types are actively used in winemaking and the production of noble cheeses (some species of the genus Penicillum).
What are the advantages of purchased material
Now the production of mycelium strains on an industrial scale has been established. The finished product has advantages:
- The cultivated grain mycelium has high germination rates.
- Compliance with the types of crops sold.
- Sterility and low disease rate.
- Affordable price.
Self-produced hyphae are 60% cheaper. In the case of oyster mushrooms (taking into account the cost of electricity, disinfection and planting material), it turns out to win an amount equal to the cost of 170 g of the product.
Transplanting stick hyphae into grain conditions is not worth it. Because you can infect cells with mold or aggressive bacteria - and the process of growing mycelium will not work. For an output of 10 kg of product, it is better to use 300–350 g of mycelium.
Conclusion
Breeding bends at home using hyphae is an effective way. This growing method is suitable for most of the Mushroom kingdom and has a high success rate.



