Existing predatory mushrooms
In nature, there are predator fungi that feed on small living organisms. There are about 200 species of such representatives of the kingdom of Mushrooms now existing. They are capable of attacking, eating and even digesting soil nematodes. For this they use special devices in their structure, which differ in a number of features from the rest of the mycelium hyphae. They adapt well to environmental conditions.
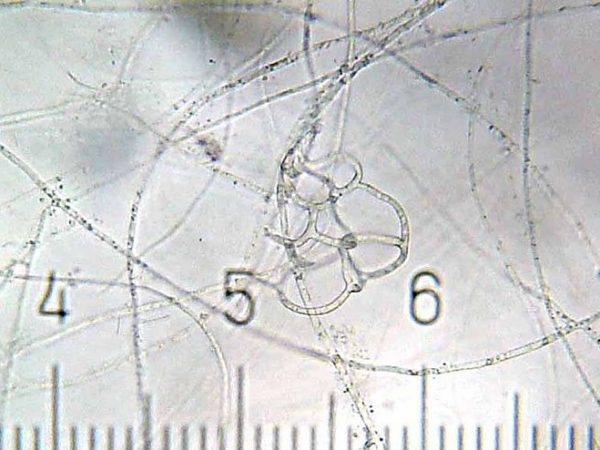
Artrobotris
Characteristic
It all started with the fact that in the 19th century Russian scientists M.S.Voronin and N.V. Sorokin, conducting research in fact in parallel, noticed rings on the mycelium of some types of mushrooms - only for what, it remained unknown until 1888. This year German scientist F.V. Zopf, after conducting a series of studies, found that these incomprehensible formations serve to catch microscopically small soil worms of nematodes. The remains of the species were found in amber.
Now the predatory mushrooms are separated into a separate ecological group. They used to belong to saprotrophs. This fact is explained by the fact that if there was no opportunity to profit from living organisms, they can also feed on dead organic matter.
They are distributed all over the world. They grow on old stumps, mosses, rhizosphere and plant roots. They also love stagnant bodies of water. They are found on soils, manure and organic residues. Release toxins.
Irina Selyutina (Biologist):
The vegetative mycelium of carnivorous fungi usually consists of branching septic hyphae with a thickness of no more than 5-8 microns. Chlamydospores are often formed in old hyphae. Traps of various structures develop on the mycelium. Often, predatory mushrooms capture animals in their traps, which are much larger in comparison with the hunter. The dimensions of the nematodes that these mushrooms are capable of catching are 0.1-1 mm, and the thickness of the fungal hyphae is no more than 8 microns (1 micron = 10-6m). Catching such a large prey became possible for the emergence of various trapping devices in the process of evolution.
In addition to nematodes, fungi prey on amoebas or other small invertebrates, but these species are less common. Food can be microorganisms such as rotifers, small crustaceans and roundworms. The predator first kills the prey, and then absorbs nutrients, the most valuable of which are nitrogen and phosphorus, which are necessary for normal life. They differ from parasitic species in that they do not settle on other organisms.
Varieties
Mushrooms are divided into groups, depending on the devices for catching small animals:
- branching hyphae with a sticky substance - protrusions are formed in species growing in water bodies;
- sticky rounded heads on the mycelium;
- the sticky mesh resulting from the branching of hyphae in the form of rings - dissolves the cuticle of nematodes, penetrates into their flesh;
- mechanical trap - mycelium cells increase, the lumen of the ring closes, the victim is compressed, which leads to its death.
Mushrooms often form a trap when the victim is nearby. They are formed even at the moment when the body of the fungus needs food or water.Sometimes nematodes can escape from the trap, but after such contact they will no longer live. For a day, only the shell will remain from the animal.
Some predators hit the prey with spores, shooting them at 1 m. Once in the body, they begin to grow and feed on it.
Examples of
Predatory fungi in most cases are mostly representatives of imperfect species, which are combined into a group called Hypomycetes, as well as Zygomycetes and some Chytridiomycetes, representatives of other taxonomic groups. These include:
- Artrobotris;
- Dactylaria;
- Monacroporium;
- Tridentaria;
- Triposporin.
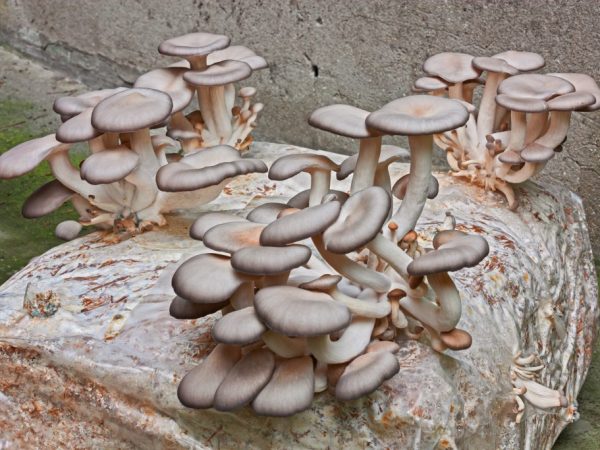

Oyster mushroom feeds on bacteria
Examples of predators:
Orbilia: it grows in rotting wood. Reminiscent of red buttons. Her hyphae take root in the soil to hunt. Some mushrooms also have this ability.
Oyster mushroom: grows on wood that cannot provide it with the necessary amount of nitrogen. The species is edible. Its mycelium form hyphae that release the toxin ostearin. It has a paralytic effect on nematodes (round soil worms), relatives of earthworms - enchitreids, shell mites. A mushroom that has caught its prey secretes enzymes. The digestion process begins. Toxins are not present in fruiting bodies, so they are suitable for human consumption.
Insectivorous arthrobotris: lives on the surface of the land, has adapted to catching representatives of springtails, or collembolans using a trap capable of capturing an insect.
Practical use
Predatory fungi are used to control pest nematodes.
When growing vegetables and champignons, biological products are used, obtained on the basis of mycelium and fungal spores. They are combined with such substrates:
- corn cut;
- composts containing straw and manure;
- mixtures of peat and straw, etc.
Dry biopreparation has proven itself to be excellent when caring for cucumbers. It is used before sowing and 2-4 weeks after it, embedded in the soil. The dosage is 300 g / m². Effectively apply the mixture when hilling bushes. In the same amount, the product is used for mushrooms. It is introduced into the hole, sowing mycelium on top.
Predatory fungi in the composition of a biological product have a positive effect on the safety of the crop. A single use of the product reduces the number of nematodes by 30-35%. When growing seedlings, occasional use allows you to kill up to 30%.
Conclusion
Mushrooms are called predatory because of their ability to feed on insects, worms, and other small representatives of the Animal kingdom. In nature, there are much more of them than plants that feed on living organisms. Their main food is soil nematodes. In the soil of these pests, there are up to 20 million / m².



