Using molds and yeasts
From the vast kingdom of Mushrooms, numbering more than 100 thousand species, molds and yeasts are the most unusual species. The potential and scope of their use by humans is extremely wide. But besides those who are useful, capable of serving for the good, there are many among them, the harm of which affects different spheres of existence.
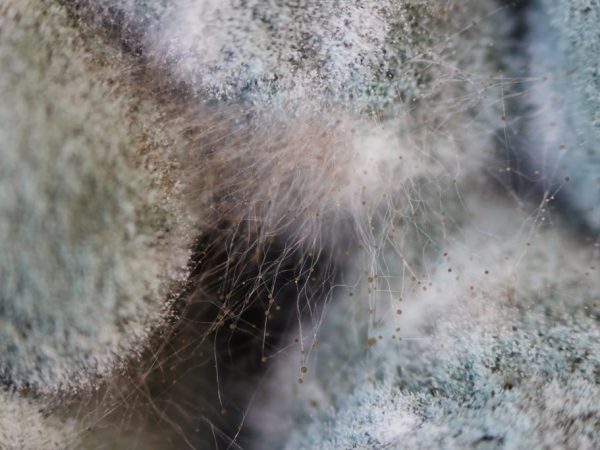

Using molds and yeasts
Research history
The invention of the microscope allowed people to study small living organisms. The Dutchman Anthony van Leeuwenhoek is considered to be the discoverer of the microworld, although the first microscope was designed by G. Galileo. A. Levenguk was the first to describe the types and forms of microorganisms. Gradually, this study resulted in a whole science that studies their structure, habitat, conditions for growth and reproduction, which is called microbiology. The founder of microbiology is considered the French scientist, L. Pasteur, who discovered the ability of microorganisms not only to process the remains of dead organic compounds, but also to purify water and soil. He also proved that fungi and yeast organisms are capable of performing functions beneficial to humans and causing harm.
With the development of microbiology, many important discoveries were made by Russian scientists: L.S.Tsenkovsky, I.I. Mechnikov, N.F. Gamaleya, D.I.Ivanovsky and others. With their help, for the first time, the foundation of the doctrine of antibiotics was laid and a science that studies viruses - virology - appeared.
At present, a lot of time and effort is devoted to the study of molds, yeasts, as well as their use and influence, opening up new opportunities for their use in many sectors of the national economy.
general characteristics
Mushrooms are tasty and healthy gifts of nature, they are found in forests and meadows, they have large fruit bodies. But science knows no less useful and more diverse of the found representatives of this kingdom - mold forms of fungi.
They appeared about 200 million years ago.
Some varieties are mycelial, consisting of filamentous formations (single or multicellular) - hyphae.
Others - to yeast (round cells), they reproduce by budding.
And the last species - macromycetes - they are traditional mushrooms in our understanding.
Mold fungi
Molds are microscopic fungi that cannot be seen with the naked eye.
Their common name is micromycetes - a group of fungi belonging to the lower and partially higher. By the type of food they are saprotrophs. Their main characteristic is the ability to process the remains of living organisms, turning them into organic and inorganic compounds. But parasites can also be found among them, such as the prostrate penicillus, settling on the surface of apples and causing them to soft brown rot.
Distribution in nature is almost ubiquitous. It is difficult to overestimate their importance in the cycle of matter and energy in the biosphere. They are not picky about living conditions: the main thing for them is warmth, high humidity and a nutrient medium. Their colonies are capable of infecting organic and inorganic substances, forming characteristic deposits.
Irina Selyutina (Biologist):
A characteristic feature of molds is the formation of mold on nutrients. It can resemble a cobweb, be fluffy or dusty, and have a variety of colors. The name of the fungus is often associated with the color of the plaque: gray mold, green mold, black mold, etc. The shape and color of the mold are systematic features. One of the necessary conditions for the formation of mold is considered to be sufficient humidity of the nutrient substrate and high relative humidity of the surrounding air. Most molds are saprophytes, but there are also optional parasites of plants, animals and humans among them. They are characterized by a very wide range of enzymes, thanks to which they can live on a variety of nutrients.
The structure of most molds, despite the diversity of their species, has common features. Their mycelium has many branches without forming large fruiting bodies. Their vegetative body consists of a large number of thin filaments - hyphae, spreading on the surface or inside the remnants of a living organism. Moreover, it can occupy large areas and grow rapidly. They are eukaryotes, that is, their cells contain a nucleus and a genetic apparatus in it, in contrast to prokaryotes, to which bacteria belong. Their cells do not contain chlorophyll, which gives plants their green color and the ability to convert carbon dioxide into nutrients.
They reproduce in the following ways:
- vegetatively: parts of the mycelium, which, spreading, begin to exist in the nutrient medium, as an independent organism;
- sexually: when two sex cells join together to form a zygote;
- asexual: with the formation of several types of spores.
Yeast
Yeast needs oxygen to live
Yeast belongs to unicellular fungi, there are more than 1500 species of representatives of ascomycetes and basidiomycetes. They are considered one of the most ancient organisms cultivated by humans. They do not have mycelium. The shape of the cell is different, and the sizes vary from 6 - 12 microns to 40 microns. These are representatives of organotrophic eukaryotes that use organic matter for nutrition in order to obtain carbon and energy for life.
They differ in that they are more demanding on nutritional conditions than molds. For the life of these unicellular organisms, oxygen is necessary, but in the absence of it, they receive energy from the alcohols formed during the fermentation process. Under anaerobic conditions, they can feed only on glucose, and in aerobic conditions, they use hydrocarbons, organic and aromatic compounds, alcohols and fats.
Yeast multiplies by division or budding or sexually, and this process under optimal conditions occurs at a high speed. Division and budding takes place through the formation and, as it grows, separation from the mother cell of a new one, which has grown to a certain size.
Types of mold and yeast
The classification of molds known to science includes more than 300 varieties. The taxonomy of the most famous of them has the following description:
- Penicilli: the most famous higher representatives of the genus of existing molds. They are found in various places, their natural habitat is soil. Includes species by way of feeding - saprotrophs and weak parasites. The division is based on the structural features of the conidiophores and depends on the layering of the brushes with conidia. The antibiotic penicillin is one of their best known products. In 1929 g.Scottish microbiologist A. Fleming first revealed antibacterial action in a representative of the genus and isolated a substance from it, which was named "penicillin". Fruiting bodies of about 40 of their species look like clestothecia, visible without special optical means and having different colors. Its mycelium is branching and transparent. Reproduces by spores.
- Aspergillus: higher aerobic molds that form fluffy, flat-shaped colonies. The mycelium has septa and is spread by spores. Extremely resistant to environmental influences. They prefer substrates enriched with oxygen and carbon - polysaccharides and monosaccharides, they also infect starch-containing species, found on bread and other food products. Aspergillus fungi differ from penicilli in that their fruiting filaments at the tops have thickenings with rod-like outgrowths, generally resembling a "shaggy head". It is from these outgrowths that the chains of spores are detached.
- Mukor: a genus of lower molds widespread in the soil, the mycelium of which is one large branched multinucleated cell that does not have partitions. The top of each of its colorless sporangiophores, reaching several centimeters in length, ends in a black head in which spores mature. These fungi form mold on food and are distinguished by their ability to cause mycoses (fungal diseases). Mukors are saprotrophs by type of food.
- Fusarium: anamorphic mold, a representative of the ascomycotaceae. Its species cause significant damage to the national economy, affecting plants and animals. Cause a variety of diseases collectively known as fusarium... Some are able to develop in symbiosis with plants, living on their roots and producing a release of substances that have a beneficial effect on the plant.
Yeast mushrooms are divided into groups according to the mode of reproduction and some other characteristics. There are nonsporogenic or asporogenic and sporogenic or sporogenic. The former are often called yeast-like and the following genera are distinguished:
- Candida: forms false mycelium and multiplies by budding.
- Torulopsis: has round and oval cells, do not form pseudomycelium and poorly ferment carbohydrates, often being pests.
- Rodotorula: multiply on food, forming pigments - red, yellow, pink and black.
Families are distinguished from the spore-forming yeast department:
- Saccharomycetes: are distinguished by their ability to ferment sugars
- Schizosaccharomycetes: used in the fermentation industry (in the production of alcoholic beverages, alcohol, vinegar, yeast, etc.)
- Sugar-code: belong to the pests of this industry.
Human use
Molds are used in many areas of human activity. Their role is especially important in the food industry and medicine.
However, they do not always bring benefits, bringing harm and losses, forcing to spend a lot of funds, efforts to combat them and their destructive impact.
In the food industry

Yeast has found its way into cooking
Mold and yeast are used in the food industry.
When baking, yeast is used - it gives the bread porosity, additional nutritional properties and increases the freshness preservation period. And the amylase enzyme added to them, secreted by the mold, improves its aroma and taste. At the same time, another enzyme - invertase - increases the shelf life of confectionery products.
For the production of alcohol, a special yeast fungus isolated from algae is used, and for wine - pure cultures of a certain type of yeast, which give it a special taste and aroma.
In the production of cheeses and fermented milk products, yeast cultures and some types of mold are used. Along with bacteria, fungi are involved in the fermentation of milk for the production of kefir.In the production of cheeses, mushrooms of the Torula genus are used for their fermentation. And their representative from the Penicillum clan, the so-called. "Noble mold", is indispensable for obtaining varieties "Camembert", "Roquefort" and "Brie", giving them a characteristic structure (with the presence of bluish mold in the thickness of the cheese mass) and a unique taste.
The quality of meat and fish products is improved by the enzyme proteinase of fungal origin. From raw and tough meat or fish of poor quality, he makes a delicate and soft product, improving its taste as well. The yeast fungus of the genus Torulopsis, added to butter, does not allow it to be affected by other types of mold, which significantly impair its taste and shorten the shelf life. And aspergillus, whose conidia look like black mold, produces citric acid.
In agriculture and other industries
In agriculture, molds and substances derived from them are also widely used. Trichodermin obtained from them successfully inhibits the growth of pathogenic microorganisms that infect plants. Some types of molds that are dangerous to insect pests are used in the fight against them. Some fungi of the genus Fusarium promote plant growth and increase their productivity.
However, among them there are also many parasites responsible for spoilage and shortening the shelf life of products, emitting toxins in the course of their vital activity. They can even lead to spontaneous combustion of flammable products - hay, straw, forage crops. Pesticides are used to combat them.
Medical use
Molds are widely used by humans for medicinal purposes. The help of their representative, penicillum, is invaluable in creating the antibiotic penicillin, the appearance of which helped save the health of millions of people. Today, one of the most popular and effective groups of them are cephalosporins. The development of microbiology made it possible to conduct tests in which, by treating molds with chemical mutagens, their new forms were obtained - ancomycetes that produce penicillin, streptomycin and produce other antibiotics in large quantities.
Equally important drugs derived from molds are statins used to lower cholesterol and treat atherosclerosis.
The use of yeast in medicine is no less important. In dried form, they are used to obtain medicines and dietary supplements, in liquid form, they are used to treat allergies and restore the microflora of the gastrointestinal tract.
Pathogenic fungi and control measures
The temperature and humidity conditions of our houses in some cases are good for the reproduction and life of fungal mold.
A person often has an allergic reaction to mold fungi. The effect of black mold in the home is the release of toxins. They enter the respiratory tract, undermining health and provoking various complications. To destroy black mold, disinfection is carried out using agents that destroy harmful strains and measures to combat dampness.
Poisoning with moldy food is also dangerous. The most dangerous of them is the yellow Aspergillus mushroom, which tends to grow on a variety of food substrates - legumes and oilseeds, cocoa, coffee, dried fish, jam.
Even in the high-tech production of polymer materials, an important task is to protect them from biological damage by pathogenic molds. Determining the parameters of the resistance of polymers to such agents helps prevent their degradation and increase the service life.
Conclusion
Information about the development of the science of microbiology and the facts revealed by it is constantly updated. The human task is to direct the properties of molds in the right direction.



