The structure and activity of the penicillus fungus
The penicillus fungus is the most common of all fungal filamentous fungi. The genus Penicillus includes a large number of species that are cosmopolitan and are more confined to the soils of northern latitudes. It is present everywhere. It is a producer of a drug from the group of antibiotics - penicillin.
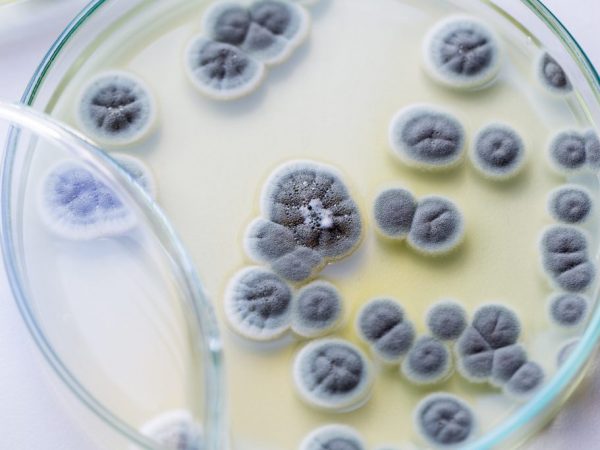
The structure and activity of the penicillus fungus
Botanical characteristic
It belongs to the group of molds. The fungal mycelium of the penicillus is its vegetative body. Unlike mucor, which has a unicellular structure of the mycelium, the mycelium of penicillin is multicellular, similar to that of another group of higher fungi - cap fungi. The mycelium is divided by septa - septa. The mycelium consists of a complex of hyphae, represented by chains of individual cells. Mushroom filaments, improperly branching, are often not colored. Propagated by spores that form at the ends of the hyphae in the form of brushes, called conidia. They are one-, two- and three-tiered and asymmetrical.
The genus Penicilli contains saprotrophic and parasitic organisms.
In terms of its external description and structure, the penicillus mushroom is similar to aspergillus. The fruiting bodies of penicillium fungi have been studied only in certain varieties and are microscopic closed clestothecia, spherical in shape, rigid in structure, retaining their appearance for several weeks, sometimes months. The color is different - white, yellow, orange and brown, in rare cases - black or red.
Some fungal colonies of representatives of the genus Penicillus are capable of forming sclerotia.
Types of penicillic colonies
4 main types are conditionally distinguished:
- Velvety: in them, almost all vegetative parts of hyphae are immersed in agar (nutrient medium, substrate), on the surface of the substrate, conidiophores are located in the form of a thick mass with a velvety appearance.
- Felt, or wooltth: they have developed aerial mushroom mycelium with sterile white edges, and conidiophores branch off from aerial hyphae.
- With the presence of mycelial strands: their aerial mycelium consists of plexuses of hyphae, which rise above the surface of the soil (substrate) and bear branches with conidia.
- With the presence of cores, or bundles: Conidiophores are collected in simple aggregated bundles, creating the form of a large granular mass.
Habitat and living conditions
Distributed everywhere, including on the ground, vegetation, also indoors, often settles on food and is able to be active, even while in the air. Among the preferred habitats are soil in temperate climatic zones. In this case, the fungal mycelium settles directly on the surface of the substrate or is completely immersed in agar, when only erect or ascending spore-bearing mushroom filaments - conidiophores - are visible at the top.In the process of growth, it forms large colonies with a certain density.
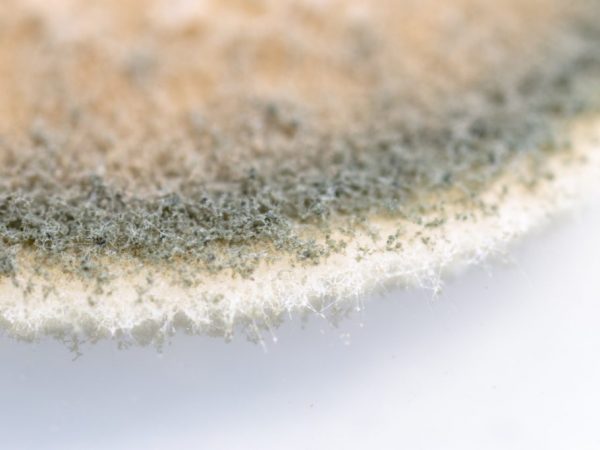

The fungus is ubiquitous
An example of the appearance of penicillus on plant foods is green mold.
Most varieties develop at temperatures between 0-5 ° C. There are those that remain active and grow at 37 ° C. Many people need a high concentration of oxygen to support their vital processes.
Species related to parasites feed by absorbing ready-made substances from living organisms. Penicillus species feed on organic debris from dead organisms, food, fruits, leading to decay. In the process of feeding, molds initially secrete digestive enzymes to break down organic matter to the simplest state.
Harm
It is capable of having a negative effect, but it is applicable in the pharmaceutical and food industries.
Due to the high concentration of enzymes contained, the parasitic fungus leads to spoilage of food and participates in the decomposition of animal and plant tissues, harming health and causing allergic reactions. It causes great harm when agricultural products and feed mixtures are damaged if the rules for their storage are violated and favorable conditions are created for the development of penicillus.
Application
In pharmaceuticals
Molds of the genus Penicilli are a natural material for the preparation of the drug penicillin, which is a member of the antibiotic group.
Irina Selyutina (Biologist):
In the early years of production, penicillin was obtained using fungal strains isolated from natural sources (Penicillium notatum and P. chrysogenum). Then a mutant strain Q-176 with high productivity was obtained. Highly productive strains are obtained mainly with the help of potent factors - X-rays and UV rays, chemical mutagens. In 1946, penicillin was synthesized, identical to natural, biologically obtained.
Fungi produce penicillins substances that neutralize and suppress the vital activity of bacteria, preventing the development of prokaryotic organisms.
In the food industry
Some varieties are used in the food industry for cheese making. Under the influence of lipolytic and proteolytic enzyme substances contained in fungi, which have an active effect on milk fats and proteins, cheeses acquire a loose and oily structure, specific gastronomic qualities and smell. Such cheeses - blue, characterized by a green-bluish color of the cheese mass, are obtained using some types of penicilli, the so-called. "Noble mold", for example, Penicillium roqueforti.
Conclusion
Penicilli mushrooms are among the molds. Leads to mold growth on organic foods and enriched humid environments. They are capable of causing harm to health. They are used for pharmacological purposes and produce penicillin that kills bacteria, and are also used in the food industry as an enzyme in cheese making.



